8:00 - 17:00
admin@hyorimvina.com.vn
Electro-sorption Process
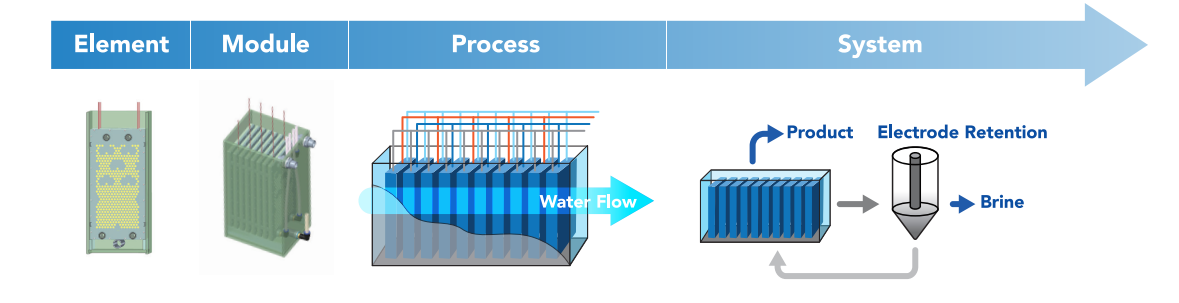
IEM
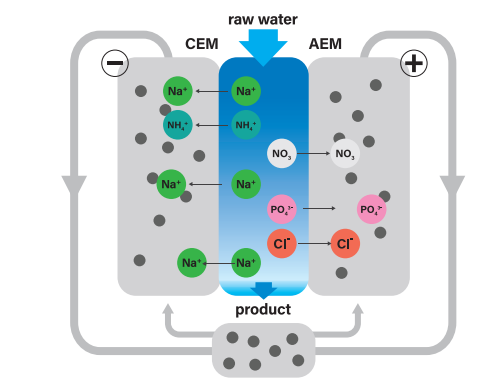
Ion-exchange membranes are semipermeable membranes that transport certain charged ions from one side to another, permitting selective passage of ions based on their charge and size.
Ion-sorption
Ions in water can be selectively adsorbed, concentrated, and removed using optimized supercapacitor electrodes. When a voltage is applied across the electrodes of a supercapacitor, from the electrolyte solution accumulates (adsorb on the surface of the electrodes, creating a double layer of charge, and energy is stored.
Ion desorption is the opposite process of ion-sorption, where the accumulated ions on the surface of the electrodes are released (desorb) back into the electrolyte.
This typically happens when the supercapacitor is discharging, i.e., when it is providing energy to an external circuit. The energy that was previously stored is released as the ions migrate back into the electrolyte and the electric field within the supercapacitor decreases.
An up-flow fluidized bed process is a specific form of the fine electrode separation. In a fluidized state, the particles exhibit fluid-like behavior, such as the ability to flow and mix. The particles can be of various types, including fine powders, granular substances, or larger pieces, depending on the application. When it comes to solid separation, an up-flow fluidized bed can be a very efficient way to separate particles based on their size, density, or shape.
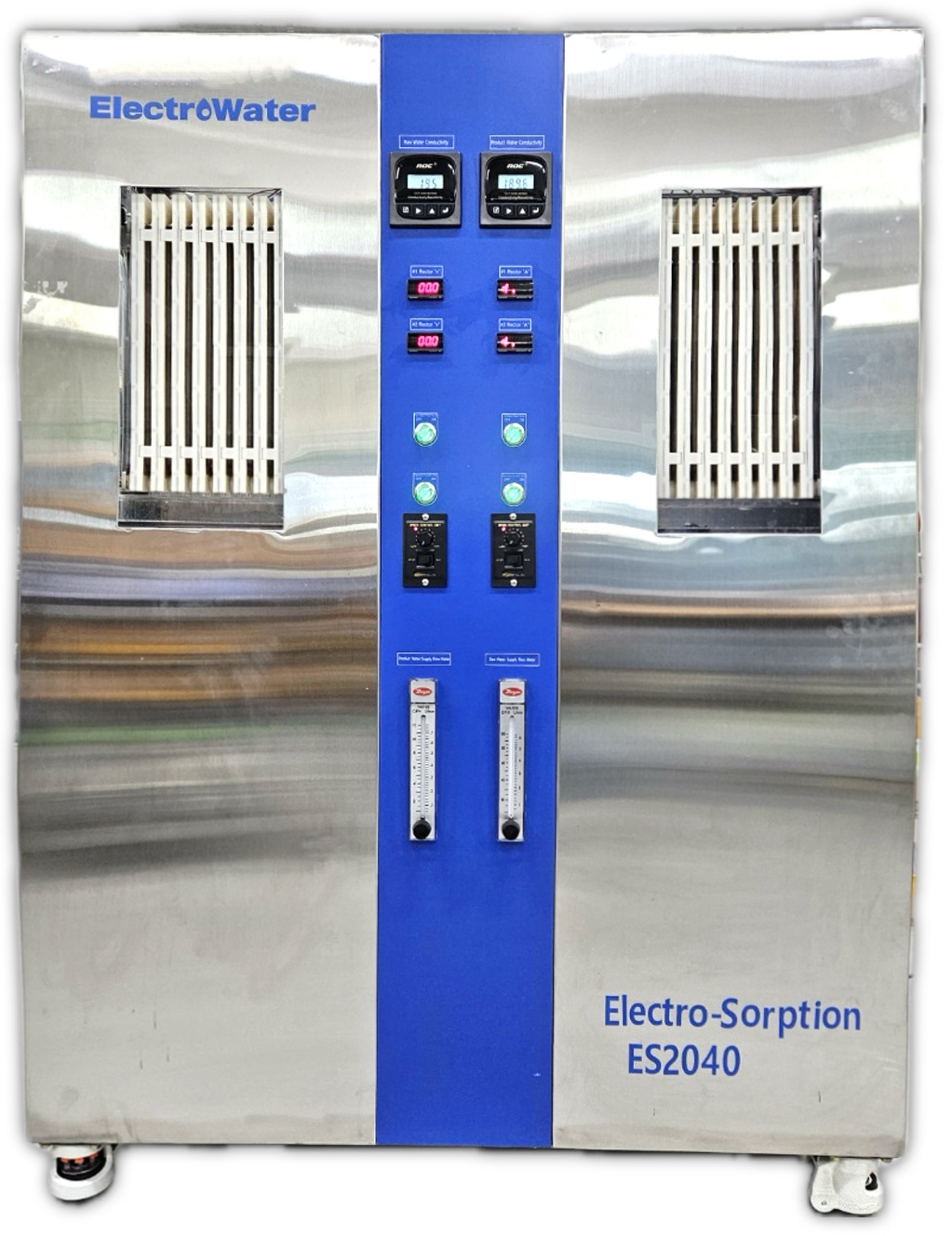
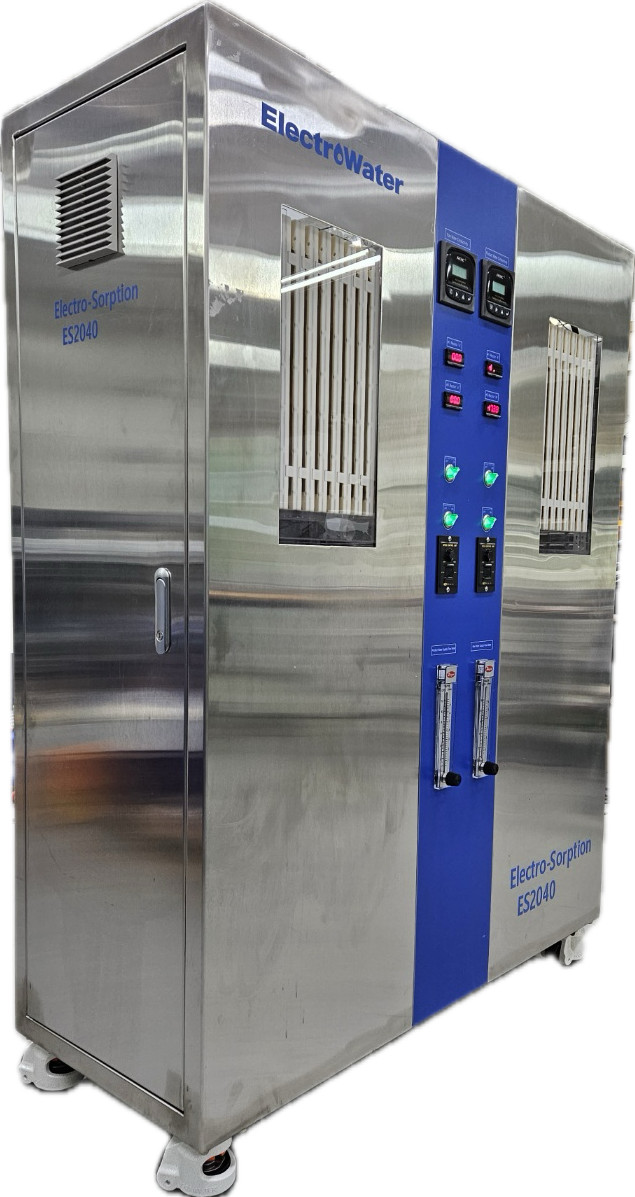


Electro-Sorption Pilot
Copyright © 2024 Hyorim Vina | All Rights Reserved | Thiết Kế Website: Phương Nam Vina